Have you ever found yourself in the middle of a Supply Chain or Logistics meeting? Lost in the jumble of acronyms and fancy business jargon; FIFO and LIFO and 3PL and Chassis? Maybe you still just can’t understand that last five-letter acronym they say a hundred times?
With many industries experiencing the rise of supply chain management and logistics, everyone is learning new terms and how they shape what it means to be an industry leader.
Below is a comprehensive list of terms and abbreviations you should know before entering the supply chain industry.
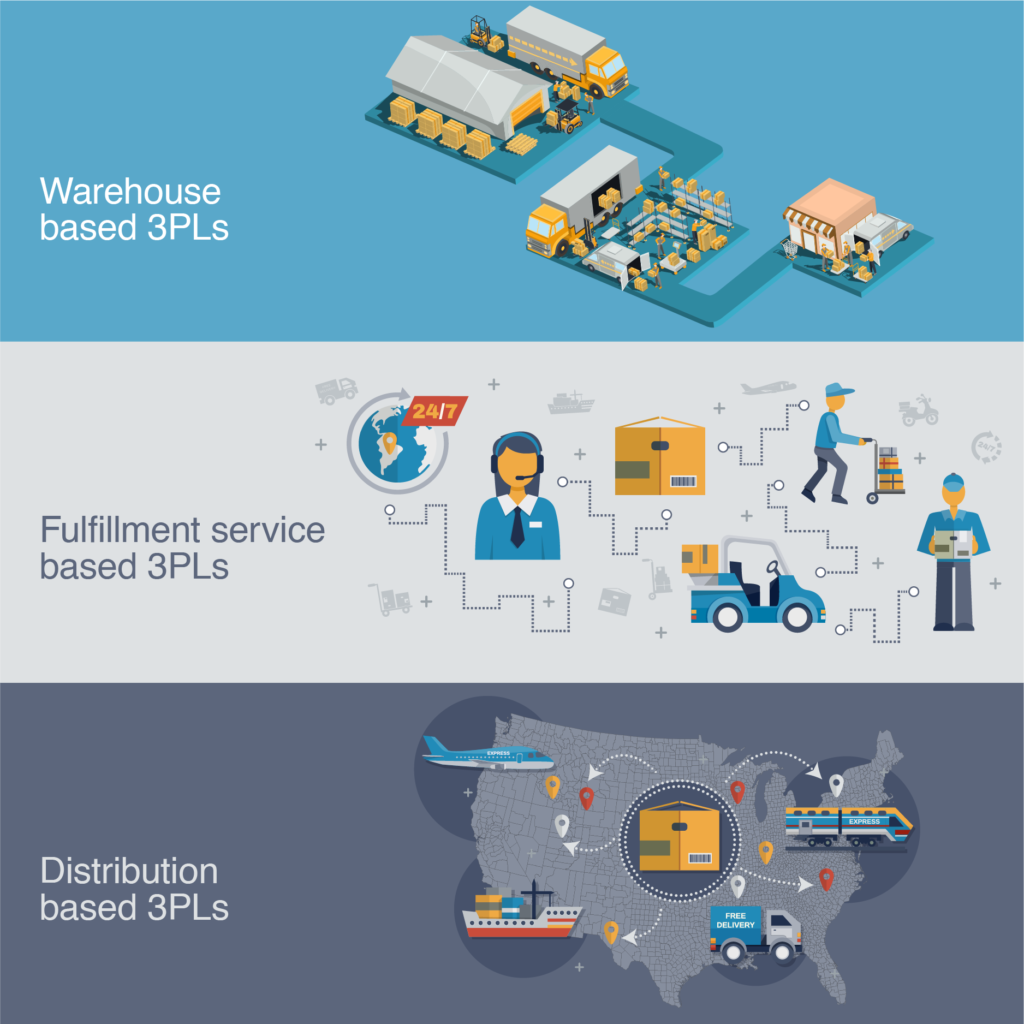
3PL:
Third-Party Logistics; an organization’s use of a third-party business to outsource elements of its distribution, warehousing, and fulfillment services.
Similarily there are 2PLs (Two-Party Logistics) and 1PLs (One-Party Logistics).
Agile Supply Chain:
A system of product distribution concerned with doing things quickly, saving costs, being responsive to market demands while maintaining flexibility and keeping productivity high.
ATA (American Trucking Associations):
American Trucking Associations is the largest and most comprehensive national trade association for the trucking industry.
BCO:
Beneficial Cargo Owner; refers to the importer of record, who physically takes possession of cargo at destination. However, it does not act as a third party in the movement of such goods.
Bill of Lading:
A Bill of Lading (BOL or B/L) is issued to a shipper and details the method and path of a shipment. It is a contract for the movement of the goods and serves as a receipt for the cargo. It can act as the transportable goods’ proof of ownership.

Carrier-For-Hire/ For-Hire-Carrier:
Any person or company who provides the transportation of passengers, regulated property, or household goods for compensation. For-hire carriers are required to get a Department of Transportation (DOT) number and a Motor Carrier (MC) number when transporting passengers or goods between states.
Carrier Haulage:
When an ocean carrier has been contracted with a customer to deliver the container to a named door destination therefore making the ocean carrier responsible for the drayage of the container to that named door location. AKA Store Door Delivery.
A steel frame with wheels that connects to a semi-truck for the transporting of a cargo container.
A location where chassis contributed by either one or several chassis owners are stored and available for use.
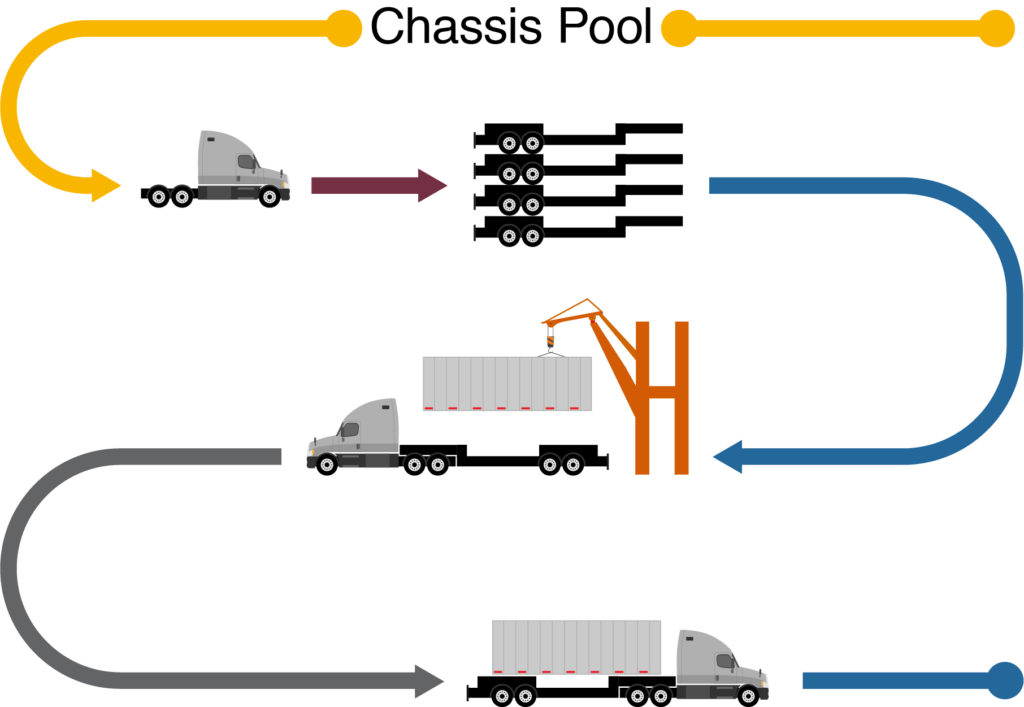
Chassis Split:
A chassis split fee occurs if the trucker has to make an additional trip to pick up a chassis, from a separate location.
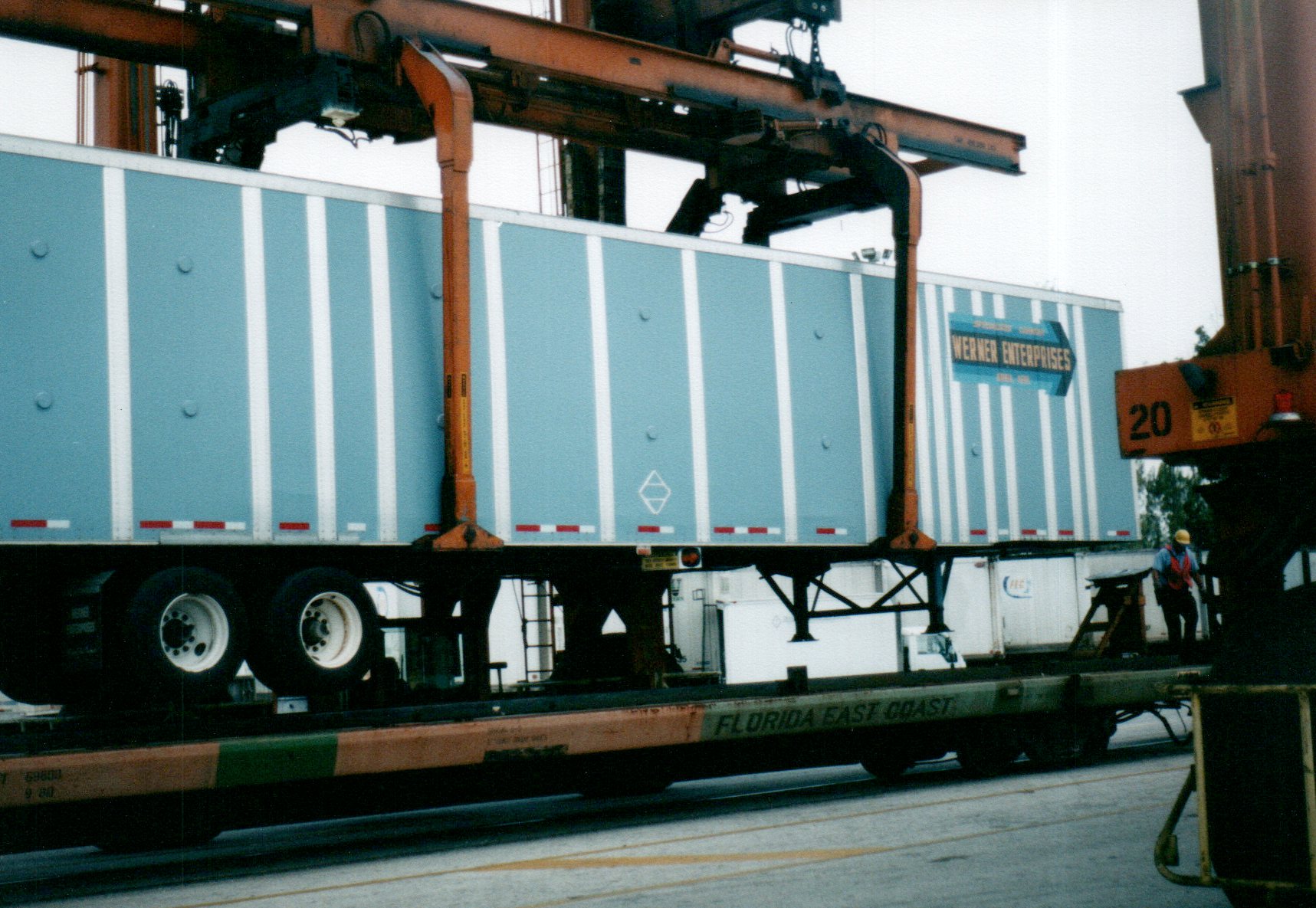
COFC (Container on Flat Car):
A container, either domestic or international, being moved on a rail flat car, and even sometimes a well car, without the chassis. These containers can also be double stacked.

Cold Chain:
Temperature-controlled supply chain. Cold chains can be unbroken, meaning an uninterrupted chain of refrigerated production, storage and distribution activities.
Common Carriers:
A person or company that transports goods or passengers on regular routes at set rates.
Container:
A steel receptacle used to transport ocean and rail shipments. Common container sizes include 20,’ 40,’ 40’ High Cube, and 45’ High Cube.
Container Allocation:
The act of allocating the volume of containerized cargo amongst a company’s contracted ocean carriers. This is generally done based on volume by origin and destination and based on the MQC of said contacts.
Demurrage:
The fee assessed by a container terminal if your cargo remains at port after the Last Free Day.
Detention:
Detention, also known as per diem, is a fee for the extra days a container is away from port.
Drayage:
The transport of goods over a short distance. Typically referred to when moving ocean and/or intermodal containers from one point to another. It is often part of a longer overall move, such as from a ship to a warehouse.
DVIR:
Driver Vehicle Inspection Reports (DVIR) are federally mandated post-trip reports in which motor carriers communicate to their equipment provider any defects that might have been noted in the post-trip inspection. Drivers are only required to document actual defects and do not need to submit a DVIR for equipment without defects or deficiencies.
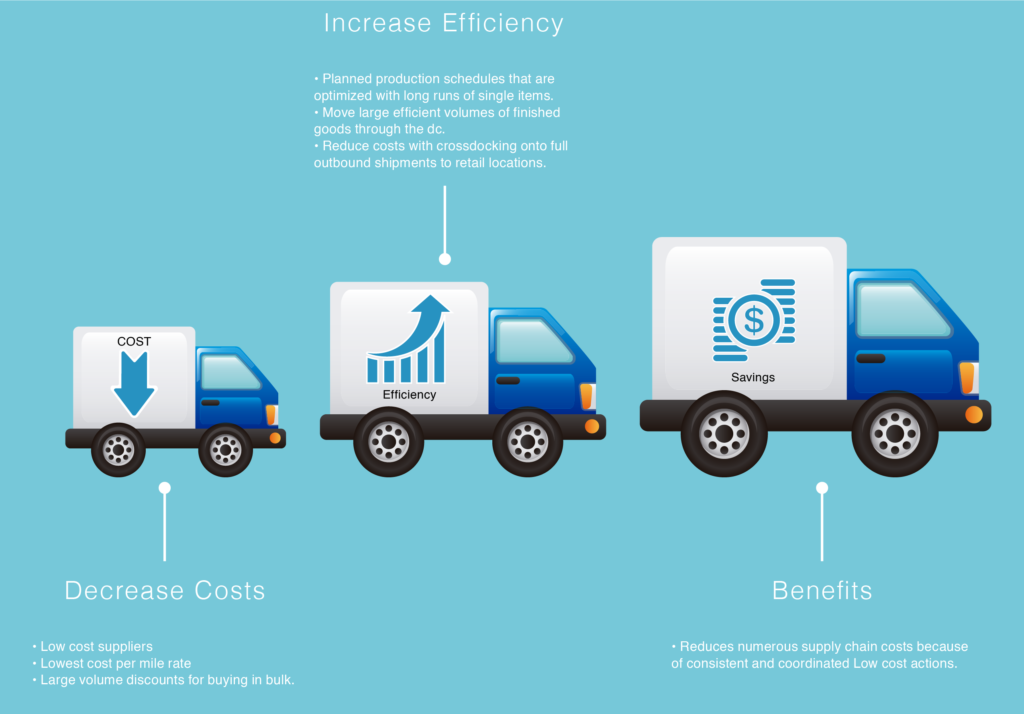
Efficient Supply Chain:
Strategies aimed at creating the highest cost-efficiency for a supply chain.
EIR:
EIR’s are usually used at the handover points. This abbreviation stands for Equipment Interchange Receipt. They are receipts for the handover of containers, trailers, chassis and similar cargo transport units and items of equipment.
Flip:
When a container is picked up off of the ground or a chassis and mounted on another chassis for transport. Shippers or truckers can assess charges when a flip occurs. See video.
FIFO:
First in First Out; method of cost lot tracking where items are valued and sold in the order they were purchased.
FTL:
Full Truck Load; the shipment will take up an entire truck by itself.
GIER (Global Intermodal Equipment Registry):
GIER provides a database of North American chassis that enables electronic equipment marking to identify the Intermodal Equipment Provider responsible for the maintenance and repair of the equipment under the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) regulations (Section 390.21, Part 390). There are currently over 660,000 chassis registered in the GIER database, representing over 100 Intermodal Equipment Providers.
House Bill of Lading:
A House Bill of Lading (HBL) is a Bill of Lading created by an Ocean Transport Intermediary (OTI) such as a freight forwarder or non-vessel operating company (NVOCC).
IANA (Intermodal Association of North America):
In Gate:
The date and time associated with a chassis arriving back to its determined drop point. Associated with the Off Hire date and time.
Intermodal:
Involving two or more different modes of transportation in conveying goods.
Just in Time (JIT) Production:
Workflow methodology aimed at reducing flow times within production systems, as well as response times from suppliers and to customers. It allows increased productivity while lowering costs.
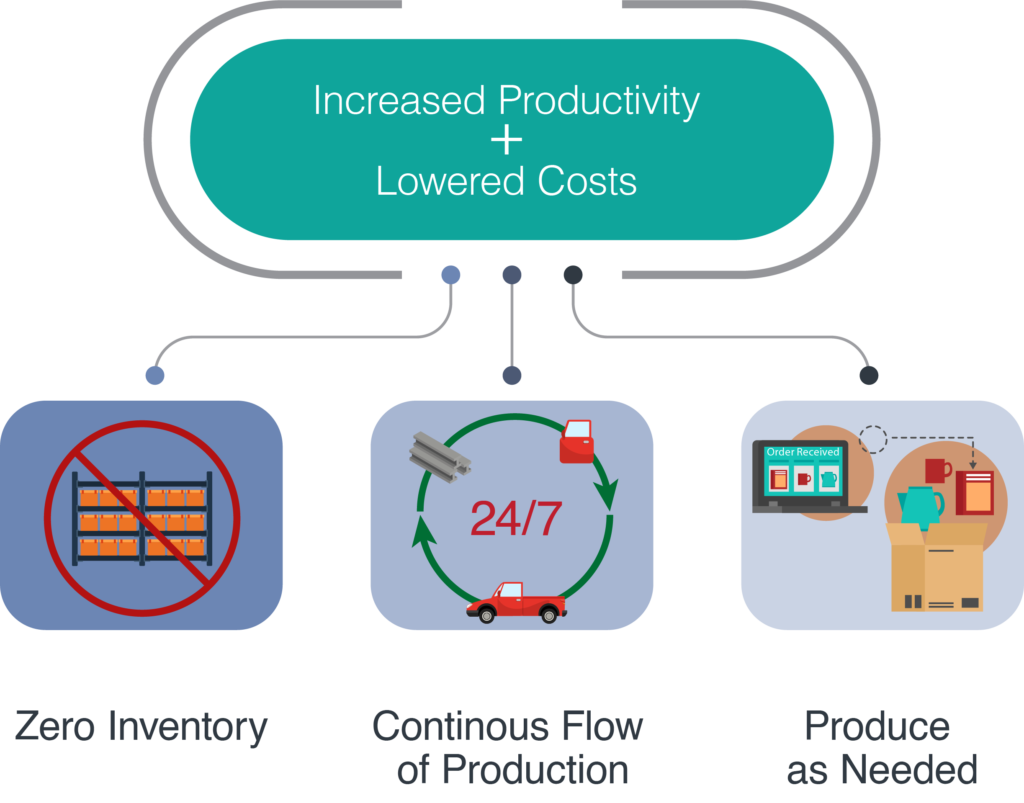
Last Free Day:
The last day of free storage time that shipments allow. The last free day is applicable at a container terminal, intermodal rail yard, airport, or once the shipment arrives at the final destination.
LIFO:
Last in First Out; A method of cost lot tracking where your most recent purchases are sold first (opposite of FIFO).
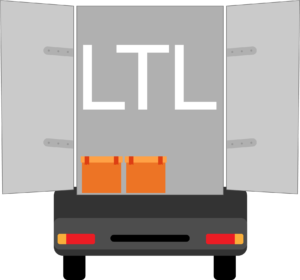
LTL:
Less Than (Truck) Load; transportation of relatively small freight.
Merchant Haulage:
When an ocean carrier has been contracted with a customer to deliver the container to a named port (cy) location. The customer, or Merchant, is responsible for the drayage of the container to the final destination.
Minimum Quantity Commitment:
Otherwise known as the MQC, this is the minimum volume of container cargo a BCO agrees to ship with an ocean carrier on during the term of the agreement
MTO:
Marine Terminal Operator provides a variety of services to ocean carriers by loading and unloading their ships.
NVOCC:
A Non-Vessel Operating Common Carrier (NVOCC) is a firm that transports goods under its own House Bill of Lading, or equivalent documentation, without operating ocean transportation vessels.
Off Hire:
The act of dropping off a chassis and stopping the clock on the usage
On Hire:
The act of picking up a chassis and starting the clock on the usage.
Out Gate:
The date and time associated with a chassis departing the origin location. Associated with the On Hire date and time.
Per Diem Charge:
A per diem charge is a fee the ocean carrier charges for each day past the number of “free” days that the container is away from port. Per diem is also known as detention.
Private carriers:
A company that only transports its goods.
Reefer:
A truck or van that has a refrigerated unit; also known as a refrigerator truck.
Responsive Supply Chain:
Strategies aimed at being flexible to the changing needs of customers.
Risk Hedging Supply Chain:
Hedge against supply, demand, and price risks by applying a variety of financial and contractual tools.
SCAC:
The Standard Carrier Alpha Code, a two-to-four letter identification, is used by the transportation industry to identify freight carriers in computer systems and shipping documents such as Bill of Lading, Freight Bill, Packing List, and Purchase Order.
Street Turn:
When one trucking company turns a chassis over to a different trucking company without returning the chassis to the depot or port.
TL:
Truck Load; Freight shipments that need the entire space or weight limit of a truck trail.
TOFC (Trailer on Flat Car):
A traditional over-the-road, or intermodal, trailer being moved on a rail flat car. Could also be a container mounted on a chassis being moved on a flat car. Commonly referred to as “piggyback”.

Transloading:
The process of transferring a shipment from one mode of transportation to another. This is common when you cannot use one mode for the entire trip.
UIIA:
Uniform Intermodal Interchange and Facilities Access Agreement. The UIIA is the only standard industry contract that outlines the rules for the interchange of equipment between intermodal trucking companies and equipment providers (ocean carriers, railroads & equipment leasing companies). Participation in the UIIA increases operational efficiencies and eliminates the need to manage multiple interchange contracts and insurance filings.
It’s not extensive, but it’s a start. Now, armed with your new vocabulary of the supply chain industry, you’ll be able to take on the supply chain world in stride. You can add to the logistics conversation and stay up-to-date while it’s happening. Keep a lookout for our blog with more information about supply chain management and logistics.
